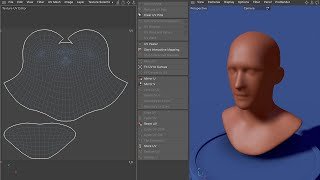
Introduction to UV Mapping
A M3DSAcademy provides beginners with the foundational skills for UV mapping, a crucial step in 3D modeling and texturing. UV mapping is the process of projecting a 3D model’s surface onto a 2D plane so that textures can be applied accurately. Proper UVs ensure that textures align correctly, maintain resolution, and prevent distortion.
Understanding UV Coordinates
UV coordinates represent a model’s geometry in a flat 2D space. U corresponds to the horizontal axis, and V corresponds to the vertical axis. Mapping 3D geometry to this 2D plane allows textures, patterns, and materials to wrap correctly around models. Beginners learn to manipulate UVs efficiently to optimize texturing workflows.
Types of UV Mapping
- Automatic Mapping: Generates UVs quickly but may require adjustments for distortion.
- Planar Mapping: Projects UVs from a single direction, ideal for flat surfaces.
- Cylindrical and Spherical Mapping: Useful for rounded objects.
- Manual/Unwrap Mapping: Provides precise control, essential for complex or organic models. M3DSAcademy teaches beginners to choose the appropriate method based on model complexity and intended textures.
UV Layout and Optimization
A clean UV layout ensures efficient use of texture space and consistent texel density. Beginners learn to arrange UV shells logically, avoid overlapping unless intentional, and maintain proportional scale to prevent texture stretching. Optimized UVs improve both performance and final visual quality.
Seams and Their Management
Seams are edges where the UV map splits, potentially causing visible texture discontinuities. Proper seam placement along natural breaks or hidden areas reduces visual impact. Beginners practice strategically placing seams to maintain smooth textures on visible surfaces.
UV Unwrapping Techniques
Unwrapping converts 3D surfaces into 2D UV islands. Techniques include pinning, relaxing, and unfolding UVs to minimize distortion. Beginners learn iterative unwrapping processes to ensure clean, predictable UV layouts suitable for detailed texturing.
Applying Textures to UVs
Once UVs are created, textures can be applied accurately. Beginners explore diffuse, normal, specular, roughness, and PBR maps to define surface characteristics. Proper UVs ensure that these textures wrap naturally across the model, enhancing realism and visual appeal.
Tileable Textures and UDIM Workflow
Tileable textures allow seamless repetition across large surfaces, useful for environments or patterned materials. UDIM workflows divide complex models into multiple texture tiles, maintaining high resolution across all areas. M3DSAcademy introduces these methods for professional-quality texturing.
Baking Textures and Maps
Baking transfers high-resolution details, such as normal, ambient occlusion, and curvature maps, onto low-poly models. UVs play a critical role in ensuring accurate baked textures without distortion. Beginners practice baking techniques to preserve detail while optimizing for performance.
Texturing Organic vs. Hard Surface Models
Organic models, like characters or creatures, require careful attention to smooth UV flow and natural textures. Hard surface models, such as vehicles or architecture, emphasize precision and alignment. M3DSAcademy teaches both approaches to develop versatile UV mapping and texturing skills.
Texture Painting and Layering
Texture painting allows artists to add color, detail, and wear directly onto models. Layering techniques enhance realism by combining dirt, scratches, and surface variation. Beginners learn to integrate painting with UV maps for consistent and visually rich results.
Common UV Mapping Challenges
Beginners may encounter stretching, overlapping UVs, or inefficient layouts. M3DSAcademy teaches troubleshooting strategies, including checking texel density, relaxing UVs, and iterative refinement to maintain high-quality results.
Optimizing UVs for Games and Real-Time Applications
UV optimization is critical for real-time performance. Techniques include minimizing seams, reducing wasted texture space, and ensuring consistent texel density. Students learn to balance visual fidelity with efficiency for games, VR, or interactive projects.
UV Mapping for Animation
For rigged characters or animated props, UVs must maintain consistency through deformation. Beginners practice proper topology and seam placement to prevent texture distortion during movement.
Integrating UVs into 3D Pipelines
UVs and textures must integrate seamlessly with shading, lighting, and rendering workflows. M3DSAcademy emphasizes organized UV layouts, proper naming conventions, and pipeline awareness for smooth production processes.
Practice Projects and Exercises
Hands-on exercises reinforce skills. Beginners create UV maps for simple objects, progressing to complex characters, environments, and hard surface models. Practice builds confidence, precision, and efficiency.
Portfolio Development
A strong portfolio showcases clean UV layouts, well-applied textures, and high-quality renders. Students are encouraged to present before-and-after examples, demonstrating problem-solving and technical skill.
Future Trends in UV Mapping and Texturing
Procedural UVs, AI-assisted unwrapping, and automated baking are streamlining workflows. Beginners gain exposure to emerging tools while mastering foundational UV mapping and texturing principles for professional readiness.
Conclusion
UV mapping and texturing are critical for transforming 3D models into visually compelling assets. M3DSAcademy equips beginners with essential skills in UV unwrapping, seam placement, texturing workflows, and optimization. By mastering these techniques, learners can create detailed, high-quality models suitable for animation, games, VR, and cinematic applications.
This article provides a comprehensive beginner’s guide to 3D UV mapping and texturing, emphasizing accuracy, workflow efficiency, and professional-quality results.